Battery-powered equipment, Spare/loose batteries and 'Smart' baggage containing batteries
This page deals specifically with batteries contained in powered equipments, called 'Portable Electronic Devices' (PEDs). We also cover spare batteries and baggage containing batteries ('Smart bags').
Table 2.3.A talks a lot about lithium ion and lithium metal batteries. Lithium ion batteries are usually rechargeable. Lithium metal batteries are usually not easily rechargeable. In this course, we usually collectively call them 'lithium batteries'. Lithuim batteries can be very dangerous and have caused hundreds of fires on aircraft worldwide. You can see graphic evidence of this by typing "plane battery fire" into a search engine. For this reason, strict restrictions apply.
There are many other types of batteries that power portable electronic devices. These batteries can be made from a variety of chemical compounds such as Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH), Alkaline and Nickel Cadmium (NiCad). Some of the more common small batteries for use in portable devices include AAA, AA, C, and 9V, just to name a few.
The quality, quantity and size of batteries that can be transported by passengers and crew is limited. The limitations apply to batteries contained in electronic devices as well as spare or loose batteries. The limitation in battery size is evaluated and measured in Watt hours (Wh) and the amount of lithuim is measured in grams (g).
All types of batteries can pose a fire hazard. Spare or loose batteries also pose a risk if not correctly insulated. Check in staff must always ask the passenger "Are you carrying any Dangerous Goods or any spare batteries?". Further questioning may be required, depending on the passenger and what hidden dangerous goods you believe they may be carrying.
It is worth noting that there are some acronyms contained in the Table 2.3.A extracts below as follows:
1. (PED) Personal Electronic Device
2. (POC) Portable Oxygen Concentrator
3. (PMED) Personal Medical Devices
Now let's have a look at each of these Table 2.3.A battery categories in closer detail.
(1) Portable electronic devices containing lithium metal or lithium ion batteries
This extract is talking about personal electronic devices (PEDs) such as laptops, mobile phones, cameras, videos, gaming devices etc plus smaller medical devices such as portable oxygen concentrators (POCs) that use smaller size batteries (not exceeding 2 g of lithium metal or 100 Wh for lithium ion batteries). A limit of 15 such devices per person applies, although the Operator may approve more.




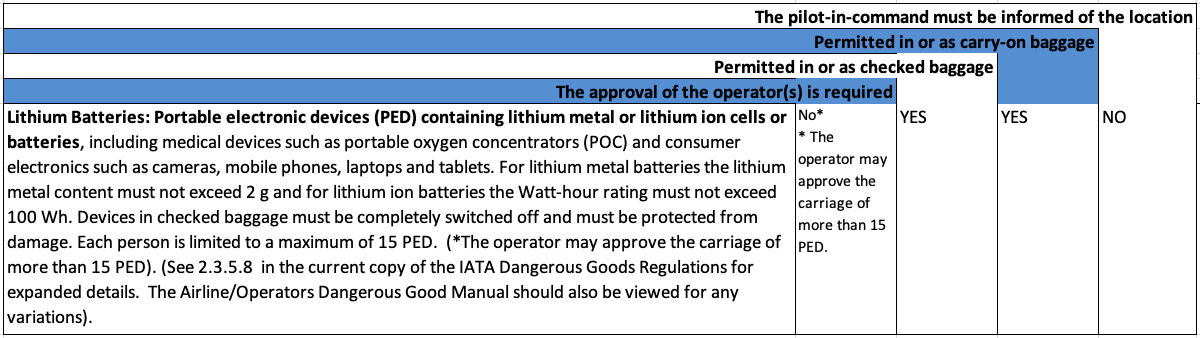
Please note from the table above:
| - |
Permitted in or as carry-on-baggage |
YES
|
|
| - |
Permitted in or as checked baggage |
YES
|
|
| - |
The approval of the operator(s) is required NB: The operator may approve the carriage of more than 15 PEDs. |
NO
|
|
| - |
The pilot-in-command must be informed of the location |
NO
|
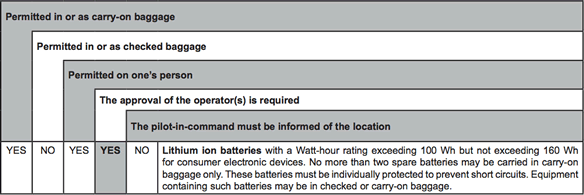
(2) Lithium battery-powered electronic devices
For portable electronic devices that use a larger lithium battery size - exceeding 100 Wh but not exceeding 160 Wh or (for medical devices only) with a lithium metal content exceeding 2 g but not exceeding 8 g.
Also note from the extract below that if the devices are carried in checked baggage, they must be completely switched off and protected from damage.
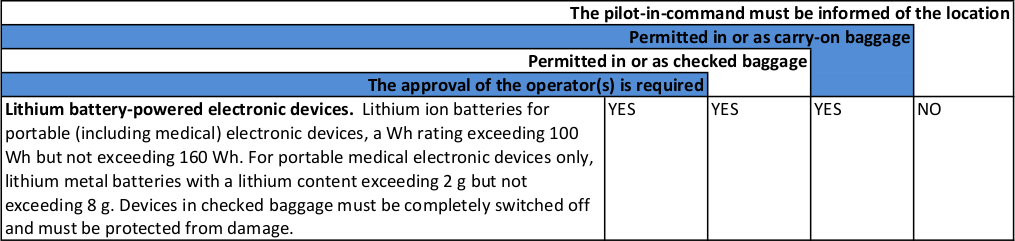
Please note from the table above:
|
- Permitted in or as carry-on-baggage |
YES
|
|
- Permitted in or as checked baggage |
YES
|
|
- The approval of the Operator is required |
YES
|
|
- The pilot-in-command must be informed of the location |
NO
|
Spare or loose batteries (3 & 4)
Where spare batteries are permitted for travel, they must travel in carry-on baggage only. Spare batteries must be protected. Thise can be achieved if the spare batteries are retained in the manufacturer's original packaging. If not in the original package, they must be insulated by placing electrical tape across the terminals, or by some other similar means such as placing each battery in a separate, sealed bag.
Let's take a closer look at the extracts from Table 2.3.A for the different kinds spare/loose batteries.
(3) Batteries, spare/loose, including Lithium batteries
This extract is talkiing about many kinds of spare batteries, such as lithium batteries, powerbanks and non-lithium batteries. Things to note from the extract below are:
- Spare batteries must be carried in carry-on baggage only. They cannot go in checked luggage;
- A maximum of 20 spare batteries is allowed under Table 2.3.A (except for wet non-spillable batteries, see next point), however the Operator may approve more;
- For non-spillable wet batteries, only two (2) spare batteries are allowed. These must be 12 volts or less under 100 Wh or less and must meet the criteria set out under Section 2.3.5.8.5 of the current IATA DGR;
- All spare batteries must be individually protected from short circuiting.




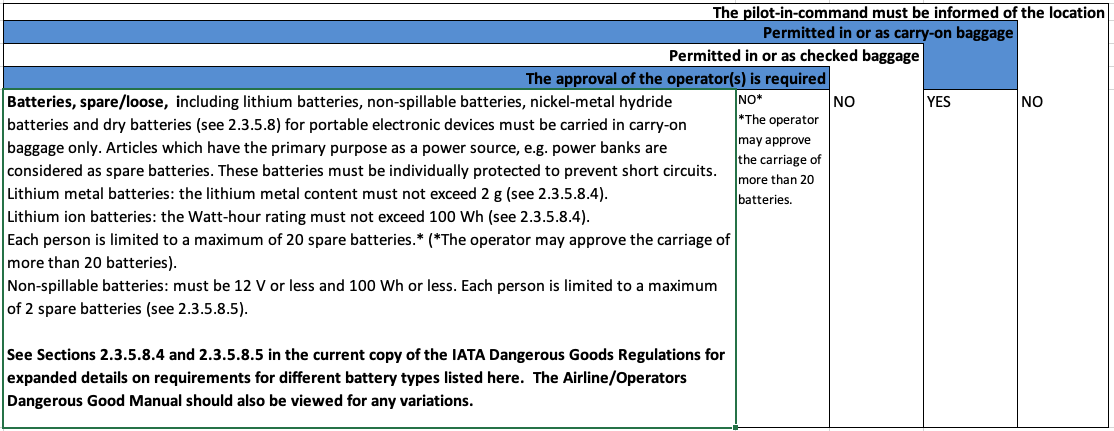
Please note from the table above:
| - |
Permitted in or as carry-on-baggage |
YES
|
|
| - |
Permitted in or as checked baggage |
NO
|
|
| - |
The approval of the operator(s) is required NB: the operator may approve the carriage of more than 20 batteries |
NO | |
| - |
The pilot-in-command must be informed of the location |
NO
|
(4) Lithium batteries, spare/loose
This extract refers to more powerful spare or loose lithium batteries. Things to note from the extract below are:
- The batteries must not exceed 160 Wh or 2 mg except when used for Personal Medical Devices (PMED). In this case, they must not exceed 8 mg lithium metal
- No more than two (2) spare batteries may be carried
- Spare batteries must be carried in carry-on luggage only. They cannot be taken in checked luggage.
- All spare batteries must be individually protected from short circuiting.

Please note from the table above:
| - |
Permitted in or as carry-on-baggage |
YES
|
|
| - |
Permitted in or as checked baggage |
NO
|
|
| - |
The approval of the operator(s) is required |
YES | |
| - |
The pilot-in-command must be informed of the location |
NO
|
Smart bags powered by batteries or powerbanks (5 & 6)
Smart bags containing powerbanks/batteries/powerpacks for charging mobile devices such as laptops, phones etc. They can only be carried on board as checked or carry-on baggage if they meet certain criteria.
Let's take a look at what Table 2.3.A says about smart bags.

(5) Baggage with installed lithium batteries:
- non-removable batteries exceeding 0.3 g lithium metal or 2.7 Wh.
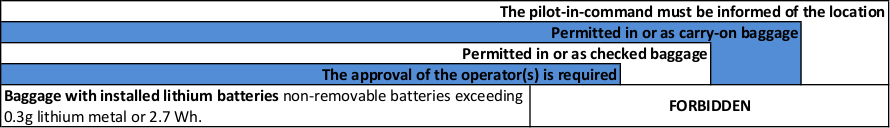
Please note from the table above:
| - |
Permitted in or as carry-on-baggage |
NO | |
| - |
Permitted in or as checked baggage |
NO
|
|
| - |
The approval of the operator(s) is required |
NO | |
| - |
The pilot-in-command must be informed of the location |
NO
|
Therefore, if the powerbank/pack exceeds 0.3 g lithium metal or 2.7 Wh and the battery cannot be removed then it is FORBIDDEN for carriage. It cannot be taken as checked baggage or as carry-on baggage.
(6) Baggage with installed lithium batteries:
- non-removable batteries not exceeding 0.3 g lithium metal or 2.7 Wh; and
- removable batteries.
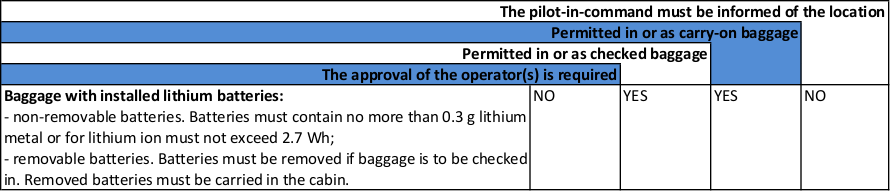
You can see from this extract that if the batteries are removable, they must be removed and carried in the cabin. They cannot go in checked luggage.
The only non-removable batteries allowed in smart bags are those that do not exceed 0.3 g lithium metal or are less than 2.7 Wh for lithium ion batteries.
Please note from the table above:
| - |
Permitted in or as carry-on-baggage |
YES | |
| - |
Permitted in or as checked baggage |
YES | |
| - |
The approval of the operator(s) is required |
NO | |
| - |
The pilot-in-command must be informed of the location |
NO
|
Always refer to the Operator's Dangerous Good Manual for specific Airline variations to the above information.

